.png)
Introduction
Brigen Consulting: Your Trusted Partner for Outsourcing Civil Engineering Services
At Brigen Consulting, we specialize in providing high-quality outsourcing civil engineering services with a particular focus on highway design. With our team of experienced professionals and state-of-the-art technology, we offer comprehensive solutions to meet the unique needs of your civil engineering projects.
The Importance of Infrastructure and Utilities in Highway Projects
Infrastructure and utilities play a crucial role in the success of any highway project. They ensure the safety, functionality, and sustainability of the roadway, while also supporting the needs of the surrounding communities.
In this blog post, we will delve into the key components of infrastructure and utilities that must be carefully considered in highway design: drainage systems, utilities coordination, and traffic control measures.
.png)
Drainage Systems: A Vital Component of Highway Projects
Drainage systems are essential for managing stormwater runoff and preventing its negative impacts on highways. By effectively channeling and removing excess water, these systems help to:
- Prevent Erosion: Erosion can weaken road surfaces, leading to potholes, ruts, and other structural damage.
- Reduce Flooding: Flooding can cause traffic disruptions, safety hazards, and property damage.
- Protect the Environment: Improperly managed stormwater runoff can contaminate waterways and harm aquatic ecosystems.
.png)
The Consequences of Inadequate Drainage
Failure to implement adequate drainage systems can result in a variety of problems, including:
- Traffic Disruptions: Flooding and water accumulation on roadways can lead to lane closures, traffic congestion, and increased accident risk.
- Safety Hazards: Standing water can create slippery road conditions, reducing traction and increasing the likelihood of accidents.
- Environmental Impacts: Stormwater runoff can carry pollutants, such as sediments, oils, and chemicals, into nearby waterways, harming aquatic life and degrading water quality.
In the next section, we will discuss the key design considerations and best practices for implementing effective drainage systems in highway projects.
Design Considerations for Drainage Systems
When designing drainage systems for highway projects, it is essential to consider a variety of factors to ensure optimal performance and long-term sustainability. Some of the key design considerations include:
.png)
Drainage System Types:
- Open Channels: These consist of ditches or swales that convey stormwater to natural or artificial outfall points. They are often used in rural areas or where land constraints are minimal.
- Pipes: Pipes are underground conduits that collect and transport stormwater to outfall points. They are commonly used in urban areas where space is limited.
- Detention Ponds: These are engineered structures that temporarily store stormwater, allowing it to gradually release into downstream channels. They are particularly effective in reducing peak flow rates and preventing flooding.

- Rainfall Intensity: The amount and intensity of rainfall in the project area will determine the required capacity of the drainage system. Historical rainfall data and future climate projections should be considered in the design process.
- Catchment Area: The size and shape of the catchment area (the area that drains into the drainage system) will influence the volume and rate of stormwater runoff. Larger catchment areas will typically require larger drainage systems.
- Soil Conditions: The type and permeability of the soil will affect the rate at which water infiltrates into the ground. Soils with low permeability will require more extensive drainage systems to prevent flooding.
- Hydraulic Gradients: The hydraulic gradient is the slope of the drainage system. A steeper gradient will allow stormwater to flow more quickly, reducing the risk of flooding.
Hydraulic Modeling and Analysis
Hydraulic modeling and analysis are essential tools for optimizing drainage system performance. These techniques involve using computer software to simulate the flow of water through the drainage system under various conditions, such as heavy rainfall or extreme events. By analyzing the results of hydraulic modeling, engineers can identify potential bottlenecks, areas of flooding, and other issues that may need to be addressed.
Installation and Maintenance of Drainage Systems

Installation Process
The installation of drainage systems typically involves the following steps:
- Excavation: Trenches or pits are dug to accommodate the pipes or structures that will make up the drainage system. The depth and width of the trenches will depend on the size and type of pipes being used.
- Pipe Laying: The pipes are laid in the trenches, ensuring proper alignment and slope to facilitate the flow of stormwater. Joints between pipes are sealed to prevent leaks.
- Connection to Outfall Points: The drainage system is connected to outfall points, such as storm sewers, ditches, or detention ponds, where the stormwater can be discharged or retained.

Importance of Maintenance and Inspection
Proper maintenance and inspection are crucial for ensuring the long-term functionality and effectiveness of drainage systems. Regular inspections can help to identify and address potential problems, such as:
- Clogged pipes: Debris, sediment, or tree roots can clog pipes, reducing their capacity and increasing the risk of flooding.
- Erosion: Erosion can damage the banks of open channels or undermine the stability of pipes.
- Structural damage: Over time, drainage systems may experience structural damage due to corrosion, wear and tear, or settlement.
By conducting regular inspections and addressing issues promptly, it is possible to maintain the integrity of drainage systems and prevent costly repairs or replacements.
Utilities Coordination and Integration: A Critical Aspect of Highway Projects
Utility Identification and Mapping
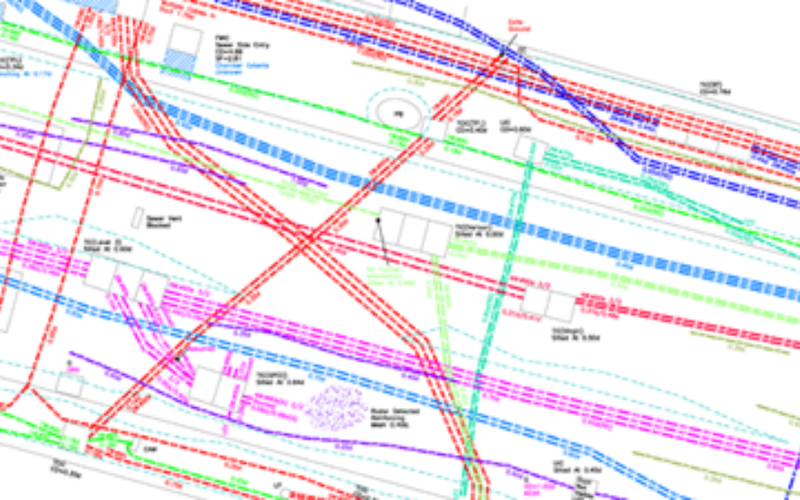
Before construction begins on a highway project, it is essential to identify and map the location of existing utilities in the project area. This includes:
- Water: Water mains and pipes
- Sewer: Sewer lines and manholes
- Gas: Gas pipelines
- Power: Electrical lines and transformers
- Telecommunications: Cable and fiber optic lines
Identifying and mapping utilities helps to prevent damage during construction and ensures that the highway project is compatible with existing infrastructure.
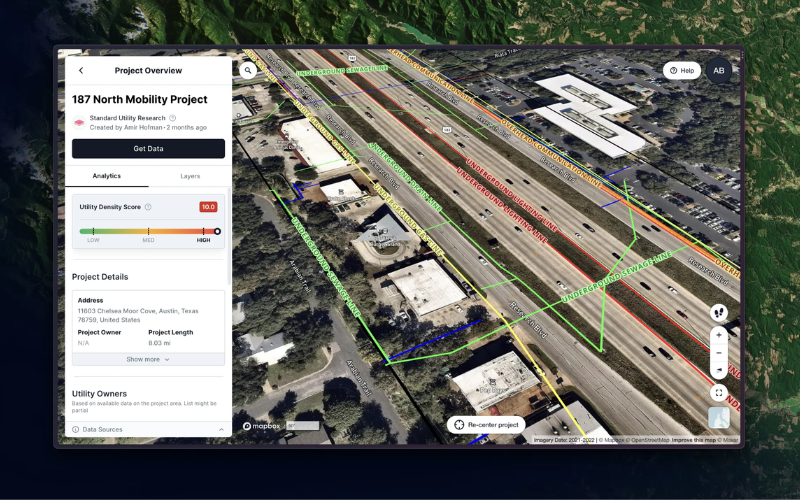
Challenges of Working with Underground Utilities
Working with underground utilities can be challenging due to several factors:
- Inaccurate data: Utility maps may be outdated or inaccurate, leading to unexpected encounters with underground infrastructure.
- Depth variations: Utilities can vary in depth, making it difficult to avoid damage during excavation.
- Multiple utilities: In densely populated areas, multiple utilities may be located close together, increasing the risk of conflicts.
To address these challenges, it is crucial to rely on accurate utility data and employ experienced professionals who are familiar with underground utility detection techniques.
Utility Relocations and Adjustments
In many cases, highway construction or widening will require the relocation or adjustment of existing utilities. This can involve:
- Moving utility lines: Relocating pipes, cables, or lines to avoid conflict with the highway construction.
- Adjusting utility depths: Changing the depth of utilities to accommodate the new road grade.
- Installing new infrastructure: Constructing new utility lines to serve the expanded area.
Coordinating utility relocations and adjustments requires effective communication and collaboration between the highway project team and utility companies. A detailed utility relocation plan should be developed, outlining the scope of work, timelines, and responsibilities of each party involved.
Utility Conflicts and Mitigation

Potential Conflicts and Damage
Despite best efforts to identify and map existing utilities, conflicts between highway construction and underground infrastructure can still occur. Common types of conflicts include:
- Damage to pipes: Excavation activities can cause damage to water, sewer, or gas pipes.
- Cutting of cables: Underground cables can be severed during excavation or drilling operations.
- Disruption of service: Damage to utilities can result in disruptions to water, sewer, gas, power, or telecommunications services.
Mitigation Strategies
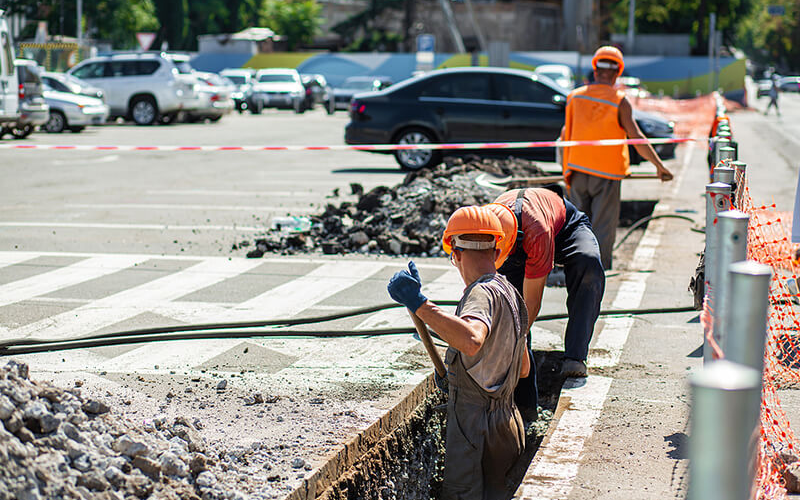

To prevent utility damage and ensure the safety of workers and the public, it is essential to implement effective mitigation strategies. These may include:
- Excavation safety measures: Using advanced detection technologies, such as ground-penetrating radar (GPR) or electromagnetic induction (EMI), to locate underground utilities.
- Hand excavation: Employing hand excavation techniques in areas where underground utilities are suspected to be present.
- Shoring and bracing: Installing shoring and bracing systems to support the ground during excavation and prevent damage to nearby utilities.
- Emergency response plans: Developing emergency response plans to address utility damage incidents promptly and minimize disruptions.
By implementing these mitigation strategies, it is possible to reduce the risk of utility conflicts and ensure the safe and efficient completion of highway projects.
Conclusion
As we have seen in this blog post, infrastructure and utilities are essential components of highway projects. Drainage systems, utilities coordination, and traffic control measures (part 2) all play critical roles in ensuring the safety, functionality, and sustainability of roadways.

Brigen Consulting: Your Partner for Highway Design
At Brigen Consulting, we specialize in providing comprehensive civil engineering outsourcing services with a particular focus on highway design. Our team of experienced professionals is committed to delivering high-quality solutions that meet the unique needs of each project.
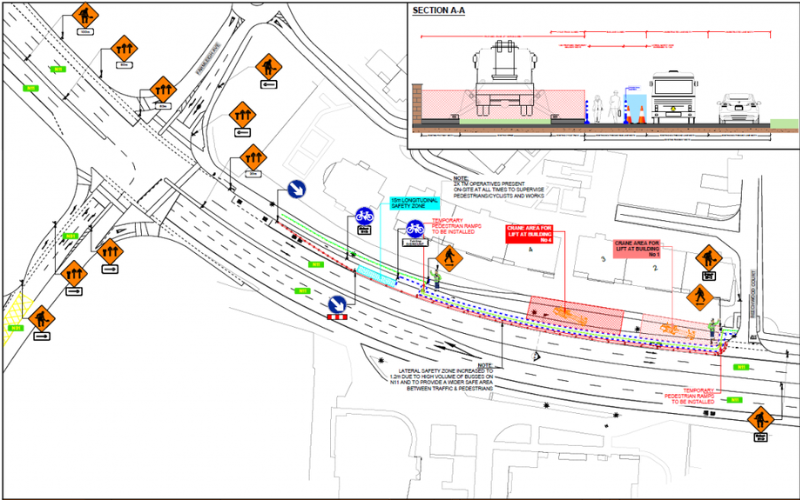
Stay Tuned for Part 2: Traffic Control Measures
In the second part of this blog series, we will delve deeper into the topic of traffic control measures. We will discuss the importance of effective traffic management during construction, explore various traffic control strategies, and highlight the role of coordination with law enforcement agencies.
Contact Brigen Consulting Today
If you are planning a highway project and need expert assistance with infrastructure and utilities, we encourage you to contact Brigen Consulting. Our team can provide tailored solutions to meet your specific requirements and ensure the success of your outsourced civil engineering projects.


























