.jpg)
A well-designed parking lot layout not only contributes to efficient space utilization but also ensures the safety and convenience of drivers and pedestrians. In this article, we will discuss the essential aspects of parking lot layouts, including different types of designs, circulation patterns, and elements that promote accessibility, safety, and user satisfaction.
Types of Parking Lot Layouts:
1. Angled Parking
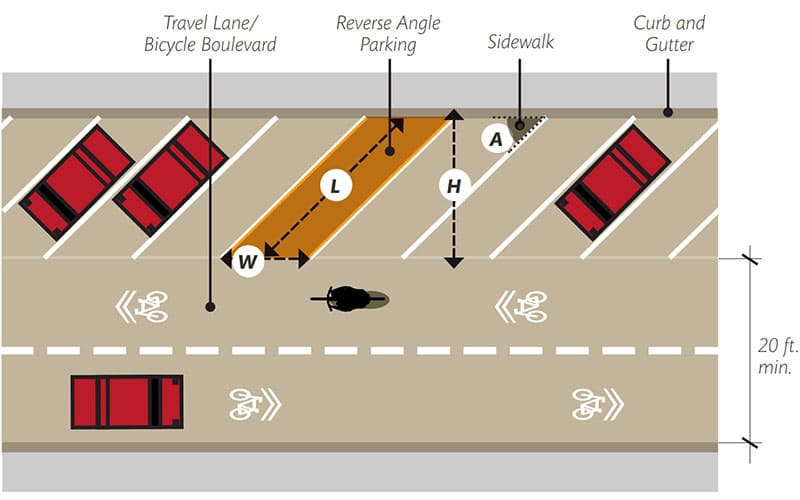
Angled parking spaces are positioned at an angle, typically between 45 and 60 degrees, to the driving aisle. This layout allows for easier maneuvering in and out of parking spaces and reduces the risk of collisions. Angled parking lots tend to have higher space efficiency than parallel parking lots, but lower than perpendicular parking lots.
2. Perpendicular Parking
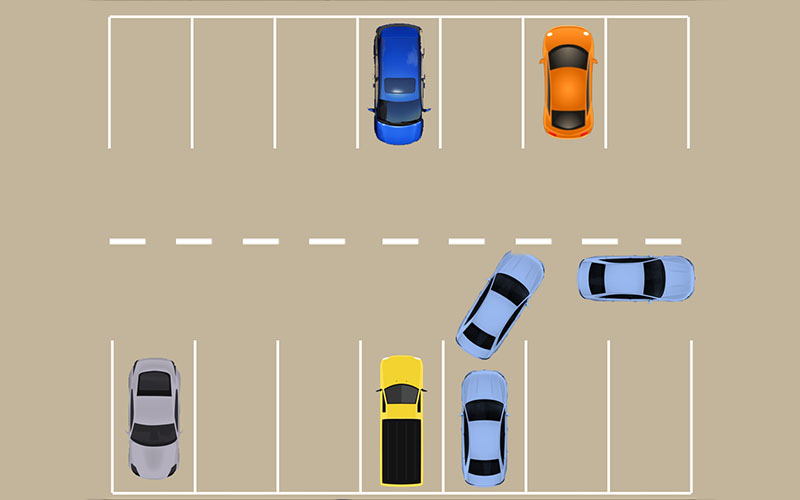
Perpendicular parking spaces are arranged at a 90-degree angle to the driving aisle. This layout maximizes space efficiency and is commonly used in large commercial parking lots. However, it requires more careful maneuvering and may result in more frequent accidents compared to angled parking.
3. Parallel Parking
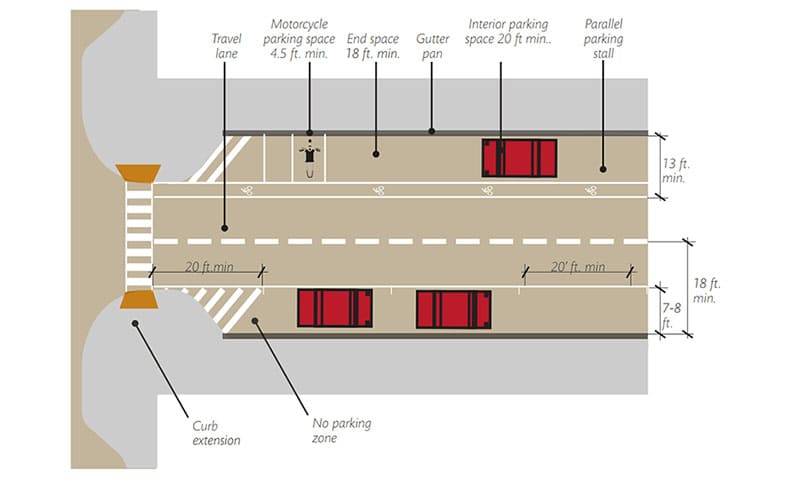
Parallel parking spaces are arranged parallel to the driving aisle. While this design is less space-efficient and more challenging for drivers, it is suitable for narrow streets or areas with limited space. Parallel parking is commonly used in urban settings and on-street parking.
Circulation Patterns:
.jpg)
1. One-Way Aisles
One-way aisles facilitate smooth traffic flow and minimize the risk of head-on collisions. They are particularly advantageous in angled parking lots, as they allow drivers to enter and exit spaces without having to turn their vehicles sharply.
2. Two-Way Aisles
Two-way aisles accommodate traffic in both directions, making them suitable for larger parking lots with multiple rows and entrances. While they offer more flexibility for drivers, they can also lead to increased congestion and a higher risk of collisions.
Accessibility and Safety Features

1. ADA-Compliant Parking Spaces
It's crucial to allocate a certain number of parking spaces for individuals with disabilities, in accordance with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). These spaces should be wider, located close to building entrances, and marked with appropriate signage.
2. Pedestrian
Walkways Incorporating clearly marked pedestrian walkways throughout the parking lot ensures that pedestrians can safely navigate the area. Additionally, installing speed bumps or raised crosswalks can help to reduce vehicle speeds and improve safety.
3. Lighting
A well-lit parking lot not only enhances safety and security but also creates a welcoming environment for users. Adequate lighting should be provided for all areas of the parking lot, including entrances, exits, and pedestrian walkways.
4. Landscaping
Incorporating green spaces and landscaping elements, such as trees and shrubs, can enhance the overall appearance of the parking lot and provide shade for parked vehicles. These elements also help manage stormwater runoff and contribute to a more sustainable design.
Conclusion
A well-designed parking lot layout strikes a balance between space efficiency, safety, and user satisfaction. By considering factors such as the type of parking arrangement, circulation patterns, and accessibility features, planners and designers can create parking lots that meet the needs of both drivers and pedestrians. Moreover, incorporating sustainable elements and prioritizing safety will contribute to a more functional and aesthetically pleasing parking environment.


























